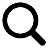Enteral feeding types encompass a range of enteral nutrition delivery methods designed to meet the unique clinical needs of patients who cannot consume food orally. The most common enteral feeding types include nasogastric (NG) tube feeding, in which a slender catheter is passed through the nose into the stomach for short-term support; nasojejunal (NJ) tube feeding, which advances the tube past the stomach into the jejunum to reduce aspiration risk; percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) feeding, a minimally invasive procedure placing a gastrostomy tube directly into the stomach wall for long-term nutrition; and jejunostomy tube feeding, which positions a tube in the small intestine for patients with gastric dysfunction or high aspiration risk. Each enteral feeding type supports continuous, intermittent, or bolus feeding regimens, offering healthcare professionals flexibility in delivering polymeric formulas, semi-elemental blends, or specialized therapeutic nutrients.
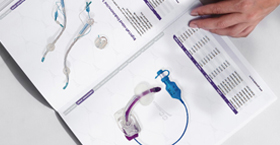
- Polyurethane Nasogastric Feeding Tubes
- Polyurethane Y-Port Nasogastric Feeding Tubes
- Funnel Transition Connector With Cap
Selecting the appropriate enteral feeding type depends on patient condition, anticipated duration of support, and gastrointestinal function. Short-term enteral nutrition often utilizes NG or NJ tubes, while long-term care favors PEG or jejunostomy tubes to enhance patient comfort and reduce tube dislodgement. Continuous feeding via infusion pumps ensures steady nutrient delivery, whereas bolus and intermittent feeding mimic natural meal patterns, promoting gastrointestinal hormone responses and improving patient tolerance. Advanced enteral feeding types feature anti-reflux valves, low-profile buttons, and weighted tips to prevent backflow, minimize discomfort, and streamline home care management.
Optimizing tube feeding success requires careful assessment of tubing materials, connector compatibility, and feeding protocols specific to each enteral feeding type. Clinicians and caregivers should monitor for complications such as tube occlusion, aspiration, and site infection, adapting feeding schedules and tube placement accordingly. By understanding the full spectrum of enteral feeding types—from nasogastric to jejunostomy—healthcare providers can personalize nutrition therapy, support gut integrity, and improve clinical outcomes. Implementing best practices for each enteral feeding type ensures safe, efficient, and cost-effective nutrition delivery for patients across acute, long-term, and home care settings.


 Français
Français Español
Español Products
Products

 About Us
About Us