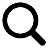Maintaining normothermia, or normal body temperature, is crucial in medical settings to enhance patient outcomes and reduce the risk of complications such as surgical site infections and prolonged hospital stays. Forced air warming blankets are widely utilized tools designed to prevent and treat hypothermia by delivering warm air to patients during perioperative care. This comprehensive guide explores the functionality, benefits, applications, and best practices associated with forced air warming blankets in patient temperature management.
Understanding Forced Air Warming Blankets
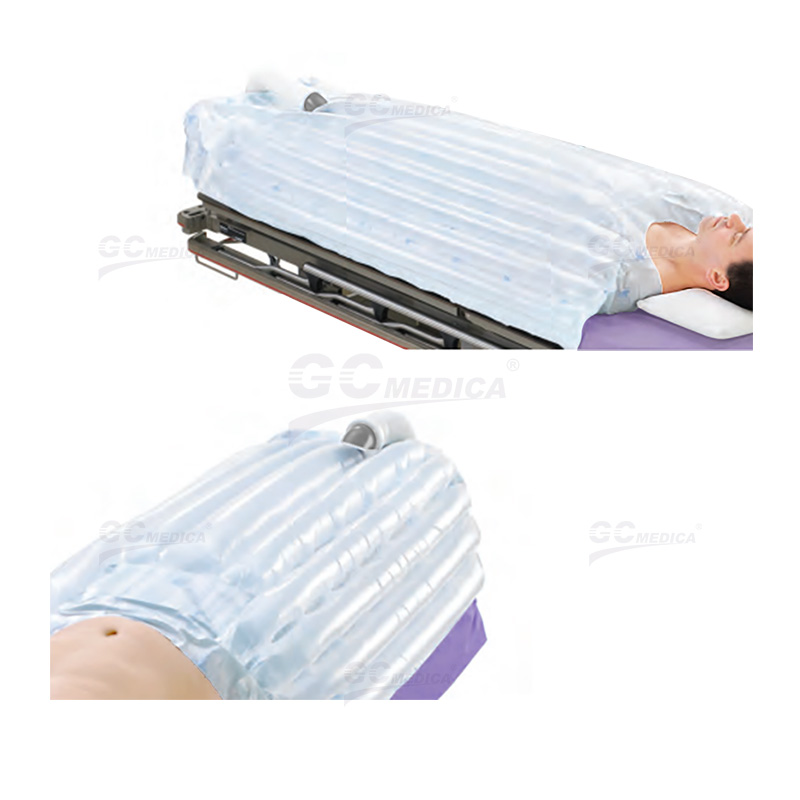
Forced air warming blankets operate by convectively transferring heat to patients. A warming unit generates heated air, which is then circulated through a flexible hose into a specially designed disposable blanket. This blanket evenly disperses the warm air over the patient's body, effectively raising or maintaining core temperature. The system typically includes a thermostatically controlled heater, a blower fan, and high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters to ensure the delivery of clean, warm air.
 GCMEDICA Closed Suction Catheters Online Promotion
GCMEDICA Closed Suction Catheters Online Promotion
Benefits of Forced Air Warming Blankets
Prevention of Hypothermia: By maintaining normothermia, these blankets help prevent the adverse effects associated with hypothermia, such as increased blood loss and higher infection rates.
Enhanced Patient Comfort: Warming blankets provide a comfortable experience for patients, reducing shivering and associated discomfort during and after surgical procedures.
Improved Surgical Outcomes: Maintaining optimal body temperature has been linked to reduced recovery times and improved overall surgical outcomes.
Versatility: These systems are adaptable for use in various medical settings, including operating rooms, recovery units, and emergency departments, catering to both adult and pediatric patients.
Clinical Applications
Forced air warming blankets are employed across multiple stages of patient care:
Preoperative Warming: Warming patients before surgery can reduce the incidence of intraoperative hypothermia.
Intraoperative Warming: During surgery, maintaining body temperature is vital to minimize complications; these blankets are used to provide consistent warmth without obstructing the surgical field.
Postoperative Warming: After surgery, continued warming aids in patient recovery by stabilizing body temperature and enhancing comfort.
Best Practices for Safe Use
To maximize the efficacy and safety of forced air warming blankets, healthcare providers should adhere to the following guidelines:
Proper Setup: Ensure that the warming unit, hose, and blanket are correctly assembled and that the blanket is positioned appropriately on the patient to facilitate even heat distribution.
Temperature Monitoring: Regularly monitor the patient's core temperature and adjust the warming unit's settings as necessary to maintain normothermia without causing hyperthermia.
Avoid "Free Hosing": Never place the hose directly under standard blankets or directly onto the patient without the designated disposable blanket, as this can lead to burns or uneven heating.
Regular Maintenance: Perform routine maintenance on the warming unit, including filter changes and system checks, to ensure optimal performance and hygiene.
Patient Assessment: Evaluate patients for contraindications to heat therapy, such as impaired circulation or sensitivity issues, to prevent adverse reactions.
Staff Training: Provide comprehensive training for all healthcare personnel on the correct use and potential risks associated with forced air warming systems to promote consistent and safe application.
Conclusion
Forced air warming blankets are essential tools in the prevention and management of hypothermia in clinical settings. By understanding their operation, benefits, and adhering to best practices, healthcare providers can significantly enhance patient safety and surgical outcomes. Implementing these warming systems effectively requires proper training, diligent monitoring, and regular maintenance to ensure their safe and efficient use in patient temperature management.


 Français
Français Español
Español Products
Products

 About Us
About Us