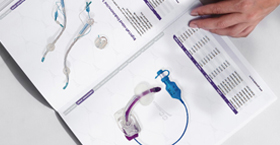
Enteral feeding tubes often include a secondary “Y-port” (also called a medication port or injection port) designed to facilitate various clinical tasks without interrupting primary feeding. Located on the proximal side of the feeding tube hub, the Y-port is positioned at an angle that resembles the letter “Y,” allowing simultaneous access for administration or monitoring while the main lumen remains dedicated to nutrition delivery.
| Function | Description | Clinical Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Medication Administration | Allows direct instillation of liquid medications into the gastrointestinal tract, bypassing the need for additional enteral devices. | Ensures accurate dosing, reduces risk of tube disconnection, and limits contamination. |
| Secondary Feeding or Bolus Delivery | Provides a conduit for rapid bolus feeds or supplemental fluids without interrupting continuous feeding running through the main lumen. | Promotes flexibility in feeding regimens and accommodates intermittent nutrition. |
| Gastric Residual and Sampling | Enables aspiration of gastric contents for residual volume checks or microbiological sampling without disconnecting the primary feeding line. | Maintains tube integrity, reduces exposure to external pathogens, and minimizes aspiration risk. |
| Contrast or Dye Injection | Facilitates introduction of radiopaque dyes or contrast agents during fluoroscopic studies to verify tube placement and monitor for leaks. | Enhances patient safety by confirming correct tube position and integrity. |
| Air Insufflation or Venting | Allows controlled introduction or removal of small volumes of air to assess gastric compliance or relieve trapped air within the feeding system. | Aids in troubleshooting occlusions and assessing gastric emptying or patency. |
Detailed Overview
Medication Administration
The Y-port’s one-way valve design permits medications—often in liquid suspension—to be introduced directly into the stomach or small intestine. This avoids the need to flush and clamp the primary feeding lumen repeatedly, reducing the risk of feed contamination or unintended flow interruptions. Clinicians typically attach a syringe to the Y-port, instill the prescribed dose, then flush with water to ensure tube patency.
Secondary Feeding or Bolus Delivery
Some patients require intermittent bolus feeds in addition to continuous feeds, such as those transitioning between enteral and oral intake. By connecting a feeding syringe or gravity bag to the Y-port, bolus feeds can be delivered rapidly through the secondary channel while the main pump continues a steady drip of nutrition.
Gastric Residual and Sampling
Monitoring gastric residual volume (GRV) remains a common practice in many care settings. Using the Y-port to aspirate gastric contents minimizes the need for tube disconnection, thereby preserving sterility and reducing aspiration risk. Moreover, sampling via the Y-port enables quick bedside microbiological or pH testing when indicated.
Contrast or Dye Injection for Imaging
In radiological confirmation of tube placement—especially post-insertion into small bowel sites—small boluses of contrast can be injected through the Y-port under fluoroscopy. This targeted approach prevents dilution of contrast in the primary feeding lumen and provides clearer imaging of the gastrointestinal tract.
Air Insufflation or Venting
Occasionally, air insufflation via the Y-port assists in verifying tube placement through auscultation (listening for air entry in the stomach). Conversely, trapped air within the tubing can be vented, helping to troubleshoot occlusions or patient discomfort due to tube-related bloating.
Conclusion
The Y-port on an enteral feeding tube serves as a multifunctional access point that enhances the versatility, efficiency, and safety of enteral nutrition therapy. By accommodating medication delivery, supplemental feeds, sampling, imaging contrast, and air management without interrupting primary nutrition flow, it streamlines patient care and minimizes infection and disconnection risks. Understanding and utilizing the Y-port’s capabilities allows healthcare providers to tailor feeding regimens, ensure accurate dosing, and maintain tube integrity—ultimately contributing to better clinical outcomes and patient comfort.
Related Products
- Polyurethane Nasogastric Feeding Tubes
- Polyurethane Y-Port Nasogastric Feeding Tubes
- Funnel Transition Connector With Cap


 Français
Français Español
Español Products
Products

 About Us
About Us