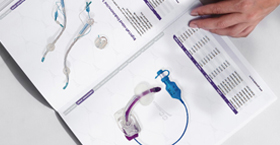
An insufflation tubing kit is a vital component in minimally invasive surgical procedures, providing a sterile pathway for the controlled delivery of medical-grade gas—most commonly carbon dioxide—into a body cavity. By maintaining a stable pneumoperitoneum or pneumothorax, the kit enables optimal visualization, working space, and organ manipulation for laparoscopic, thoracoscopic, and arthroscopic interventions. Proper selection, handling, and maintenance of the tubing set are crucial to patient safety and procedural efficiency.
Typical kits include the following components:
Insufflation Tubing: Reinforced PVC or silicone hose, often with built-in anti-kink coils, connecting the insufflator device to the trocar or cannula.
Filter & Connector Assembly: Inline bacterial/viral filter to prevent contamination of the insufflator, plus standardized Luer or proprietary fittings.
Pressure Monitoring Line: Secondary lumen or separate tube that relays real-time intra-cavity pressure readings.
Safety Valve & Check Valve: Prevents backflow of bodily fluids into the insufflator and protects against over-pressurization.
Y-Connector or Manifold: Allows attachment of suction or smoke-evacuation lines without breaking the gas circuit.
Key benefits of a well-designed kit include consistent insufflation pressure, minimal risk of gas leaks, and reduced operating-room turnover time due to rapid set-up. To ensure optimal performance and patient protection, staff must verify kit sterility, inspect for tubing cracks or discoloration, and confirm secure connections before insufflation begins. After each procedure, single-use kits are discarded according to biohazard protocols; reusable systems require validated cleaning and sterilization cycles.
Below is a concise table summarizing core features, clinical functions, and care recommendations for insufflation tubing kits:
| Feature | Function | Care & Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Tubing Material | Reinforced PVC or silicone with anti-kink coils | Inspect for tears/discoloration; replace if compromised |
| Inline Filter | Bacterial/viral filter to protect insufflator | Single-use; discard after each case |
| Pressure Monitoring Line | Relays intra-cavity pressure to insufflator display | Ensure unobstructed lumen; flush per manufacturer guidelines |
| Safety & Check Valves | Prevent backflow and over-pressurization | Test valve function during setup; replace if stiff or leaking |
| Connectors & Manifolds | Standardized Luer or quick-connect fittings; optional smoke evacuation port | Secure connections; avoid cross-threading; clamp auxiliary ports when not in use |
| Length & Diameter | 2–4 meters length; 3–5 mm internal diameter | Select appropriate length to avoid excessive dead space and drag |
By choosing the correct insufflation tubing kit and adhering to aseptic handling, pressure-verification protocols, and disposal or reprocessing guidelines, surgical teams can maintain a reliable pneumoperitoneum, minimize procedural delays, and enhance overall patient outcomes in endoscopic surgery.
| Insufflation Tubing Set with Gas Filter > |


 Français
Français Español
Español Products
Products

 About Us
About Us