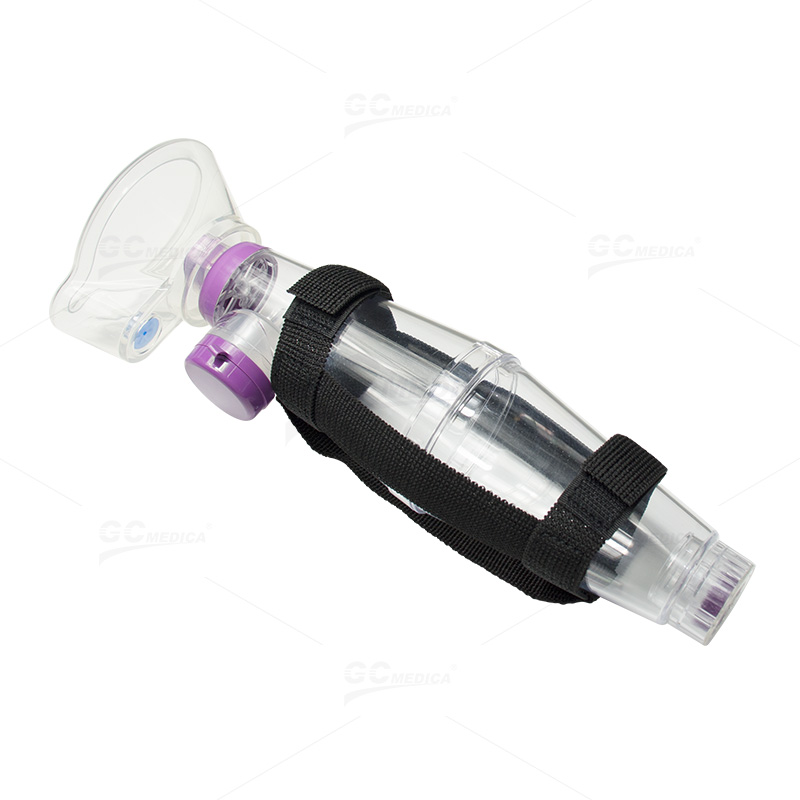
In respiratory care, the combination of a metered dose inhaler (MDI) with a spacer has become a standard method for delivering aerosolized medications effectively. This integrated approach not only ensures accurate dosage but also maximizes lung deposition and minimizes side effects. In this article, we explore the benefits and clinical applications of using an MDI with a spacer, helping healthcare professionals and patients optimize respiratory therapy.
 GCMEDICA MDI with Spacer Online Promotion>
GCMEDICA MDI with Spacer Online Promotion>
Enhanced Drug Delivery
MDI spacers are designed to bridge the gap between the inhaler's medication release and the patient's airway. By allowing the medication to be held in a chamber momentarily, these devices reduce the need for precise hand-breath coordination. This delay results in:
Improved Lung Deposition: The aerosol has more time to slow down, reducing the amount of medication that deposits in the oropharynx. More drug reaches the lungs, where it is needed.
Reduced Side Effects: With less medication depositing in the mouth and throat, common adverse effects such as hoarseness or oral thrush are minimized.
Consistent Dosing: The spacer helps ensure that a consistent amount of medication is delivered with each use, which is vital for maintaining effective disease control.
Clinical Applications
The use of an MDI with a spacer is widespread in various clinical scenarios:
Asthma Management: For both adults and children, spacers significantly enhance the management of asthma by improving drug delivery. This method is especially beneficial during acute exacerbations when rapid relief is needed.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): Patients with COPD often experience difficulty coordinating inhalation. Spacers mitigate this issue and help provide a more consistent therapeutic effect.
Preventive Therapy: Regular use of MDI with a spacer in preventive treatment regimens ensures that patients maintain control over their respiratory symptoms, reducing the frequency of emergency visits.
Emergency Care: In acute settings, such as emergency departments or urgent care clinics, spacers facilitate the rapid administration of bronchodilators and corticosteroids, ensuring swift relief for patients in distress.
Benefits for Patients and Healthcare Providers
Using an MDI with a spacer offers multiple benefits:
Ease of Use: Spacers simplify the process, making inhalation therapy more accessible, particularly for young children, the elderly, or those with disabilities.
Enhanced Patient Compliance: With improved ease of use and reduced side effects, patients are more likely to adhere to their inhalation therapy, resulting in better disease management.
Cost-Effectiveness: By optimizing the delivery of medication, spacers can reduce the need for additional treatments and hospitalizations, ultimately lowering healthcare costs.
Versatility: These devices are compatible with a wide range of inhaled medications, allowing for flexible treatment plans tailored to each patient's needs.
Best Practices for Using MDI with Spacer
To maximize the benefits of using an MDI with a spacer, consider the following tips:
Proper Technique: Ensure patients are instructed on the correct technique. They should shake the inhaler, attach the spacer, and breathe slowly and deeply after pressing the inhaler.
Regular Cleaning: Spacers must be cleaned regularly to prevent the build-up of medication residue and bacteria. Follow recommended cleaning guidelines to maintain device efficacy.
Periodic Assessment: Healthcare providers should periodically assess the patient’s inhalation technique and adjust the therapy if necessary, ensuring optimal drug delivery.
Conclusion
The use of an MDI with a spacer represents a significant advancement in respiratory care. By improving medication delivery, reducing side effects, and enhancing patient compliance, this approach plays a critical role in managing conditions such as asthma and COPD. Whether in routine care or emergency situations, integrating a spacer with an MDI leads to more effective and reliable respiratory therapy, ultimately improving the overall quality of care.


 Français
Français Español
Español Products
Products

 About Us
About Us