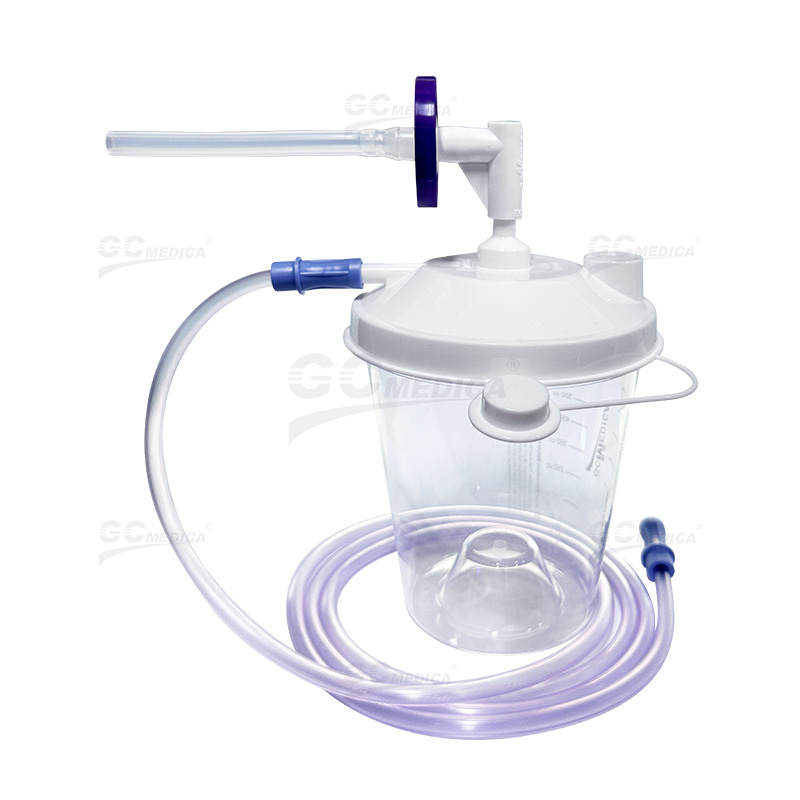
Suction canisters are essential components in medical settings, facilitating the collection and containment of bodily fluids during various procedures. The choice between disposable and reusable suction canisters impacts factors such as infection control, cost, environmental footprint, and operational efficiency. Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of each type is crucial for making informed decisions that align with the needs of healthcare facilities.
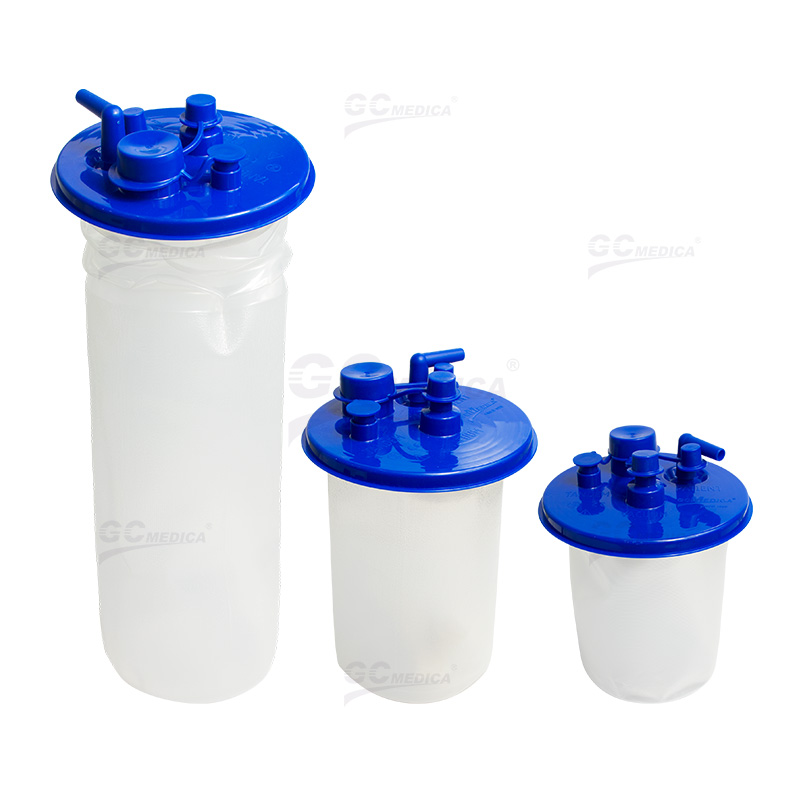
| Single Use Soft Liner | |
| Outer Canister | |
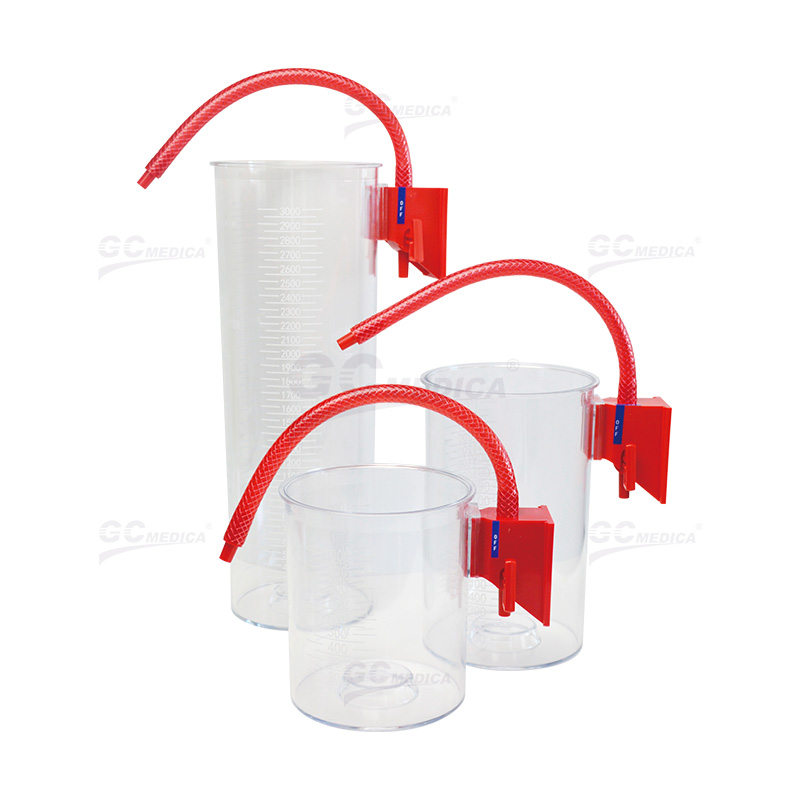
| Rigid Canister | |
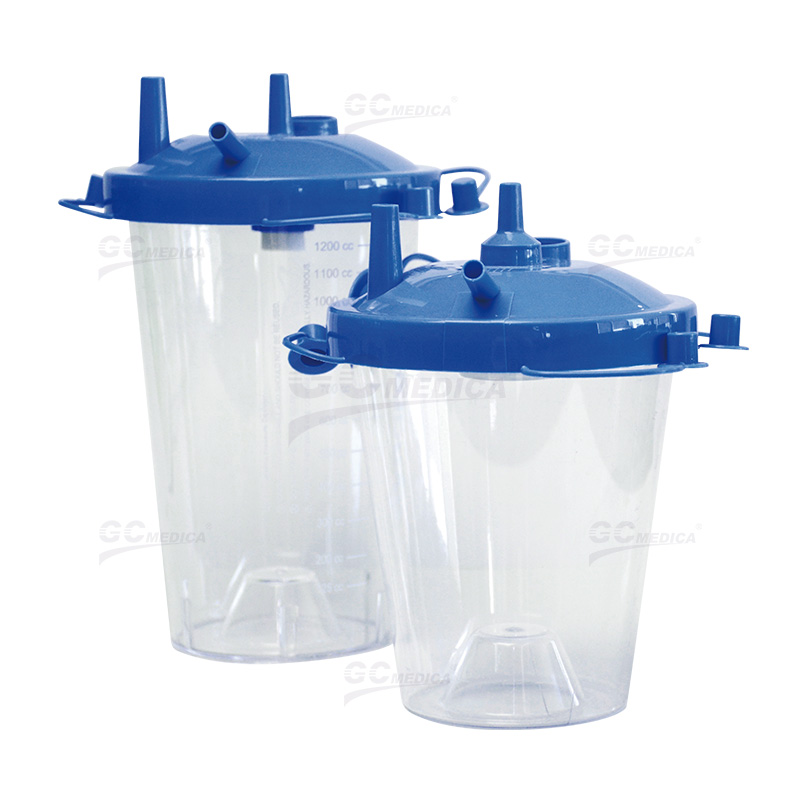
| Rigid Canister with Filter Kit |
Disposable Suction Canisters
Advantages:
Infection Control: Disposable canisters are designed for single use, significantly reducing the risk of cross-contamination and hospital-acquired infections (HAIs). After use, they are discarded, eliminating the need for reprocessing and the potential for residual contamination.
Convenience: These canisters come pre-sterilized and ready for immediate use, streamlining workflow and reducing the burden on healthcare staff. The elimination of cleaning and sterilization processes allows for more efficient turnover between procedures.
Considerations:
Environmental Impact: The single-use nature of disposable canisters contributes to medical waste, raising concerns about environmental sustainability. The accumulation of plastic waste from discarded canisters poses challenges for waste management in healthcare facilities.
Ongoing Costs: While the initial purchase price may be lower, the recurring expense of continually restocking disposable canisters can accumulate over time, impacting the facility's budget.
Reusable Suction Canisters
Advantages:
Cost Efficiency: Reusable canisters, typically made from durable materials, can be sterilized and used multiple times. This reusability can lead to cost savings over the long term, as the need for frequent replacements is reduced.
Environmental Sustainability: By minimizing medical waste, reusable canisters present a more environmentally friendly option. The reduction in disposable plastic products aligns with initiatives aimed at promoting sustainable healthcare practices.
Considerations:
Sterilization Requirements: Proper cleaning and sterilization between uses are imperative to prevent cross-contamination. This process demands strict adherence to protocols, specialized equipment, and additional labor, which can offset some of the cost benefits.
Infection Risk: If sterilization is not performed adequately, reusable canisters may harbor pathogens, increasing the risk of HAIs. Ensuring consistent and thorough reprocessing is critical to maintain patient safety.
Key Factors to Consider
When deciding between disposable and reusable suction canisters, healthcare facilities should evaluate:
Infection Control Priorities: Assess the facility's capacity to adhere to stringent sterilization protocols and the importance of minimizing infection risks.
Budget Constraints: Consider both the immediate and long-term financial implications, including purchase costs, reprocessing expenses, and potential savings.
Environmental Policies: Align the choice with the facility's commitment to sustainability and waste reduction initiatives.
Operational Efficiency: Evaluate the impact on staff workload, turnaround times between procedures, and overall workflow.
Conclusion
Both disposable and reusable suction canisters offer distinct benefits and challenges. The decision should be guided by a comprehensive analysis of infection control needs, financial considerations, environmental impact, and operational dynamics. By carefully weighing these factors, healthcare facilities can select the option that best supports patient safety, staff efficiency, and organizational goals.


 Français
Français Español
Español Products
Products

 About Us
About Us