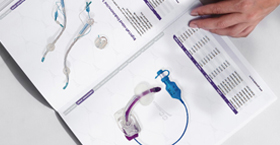
Urinary catheterization is a common medical procedure used to drain urine from the bladder when patients are unable to void naturally. To perform catheterization safely and effectively, a range of specialized supplies is required—each designed to minimize infection risk, ensure patient comfort, and accommodate different clinical scenarios. From the catheter itself to the drainage bag and ancillary accessories, quality and compatibility of each component are critical.
The most essential item is, of course, the catheter: a thin, flexible tube available in multiple materials and configurations. Foley catheters—balloon-tipped and designed for indwelling use—are perhaps the most widely used, whereas intermittent (or straight) catheters may be used for short-term drainage. Catheters are manufactured from materials such as silicone, latex, and PVC, each offering different levels of flexibility, biocompatibility, and risk of allergic reaction. In addition, proper lubrication, securement devices, and sterile drainage systems are all indispensable to prevent urethral trauma and catheter‑associated urinary tract infections (CAUTIs).
Below is a concise table summarizing the key urinary catheter supplies commonly stocked in hospitals, clinics, and home‑care settings:
| Supply Item | Material | Size Range (Fr) | Typical Use | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Foley Catheter | Silicone, Latex | 6–24 | Indwelling drainage (long‑term) | Inflatable retention balloon; radiopaque line |
| Intermittent Catheter | PVC, Hydrophilic | 8–16 | Single-use bladder emptying | Pre‑lubricated option; hydrophilic coating |
| Closed Drainage Bag | PVC | 500 mL–2 L | Urine collection from catheter | Anti-reflux valve; graduated markings |
| Leg Bag | PVC, Silicone | 300–500 mL | Ambulatory drainage | Elastic strap; low-profile design |
| Securement Device | Adhesive, Fabric | N/A | Catheter stabilization | Skin-friendly; adjustable strap |
| Lubricating Jelly | Water‑based gel | 5–60 mL | Catheter insertion ease | Sterile; reduces urethral friction |
| Antimicrobial Coating | Silver alloy, Nitrofurazone | N/A | Infection prophylaxis | Bacteriostatic surface; prolonged dwell effect |
In clinical practice, the selection of catheter supplies is tailored to each patient’s age, anatomy, and underlying condition. For example, pediatric catheters (<10 Fr) are indicated for children, whereas larger French sizes (18–24 Fr) may be used in perioperative settings or when there is gross hematuria requiring high-flow drainage. Silicone catheters are preferred in patients with latex allergy or those requiring long‑term catheterization due to their superior biocompatibility. Additionally, hydrophilic-coated intermittent catheters can reduce urethral micro‑trauma and improve patient comfort during self‑catheterization.
Ultimately, reliable access to high‑quality urinary catheter supplies is foundational to both acute care and chronic management of urinary retention. Proper staff training in aseptic techniques, routine inspection of catheter components, and adherence to replacement schedules all contribute to minimizing complications. By understanding the features and appropriate applications of each supply item, healthcare providers can improve patient outcomes, reduce infection rates, and enhance overall comfort for individuals requiring catheterization.
| Urology Supplies > |


 Français
Français Español
Español Products
Products

 About Us
About Us