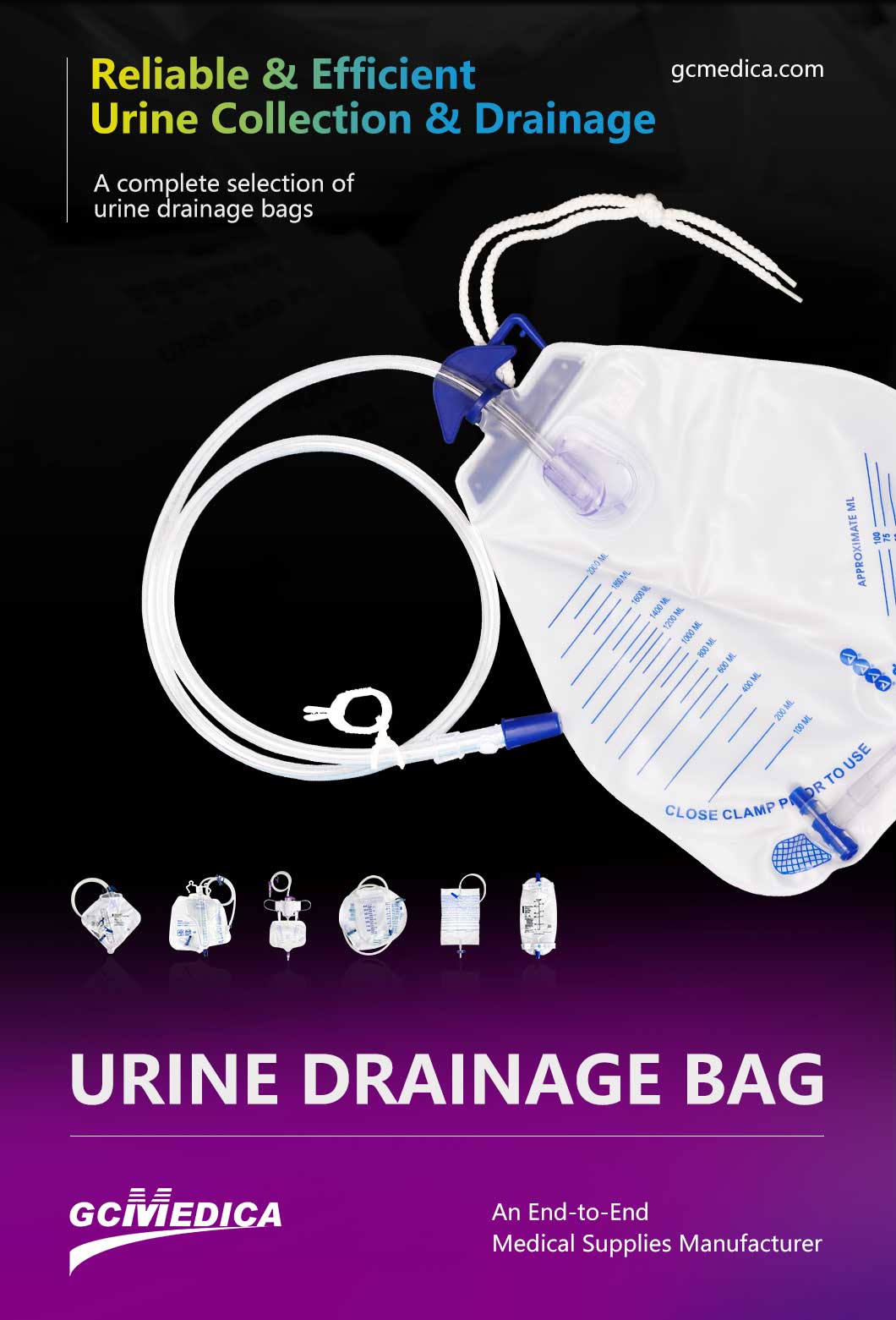
A closed-system urine drainage bag is an indwelling catheter setup designed to maintain a sterile, sealed pathway from the bladder to a collection reservoir. By preventing breaks in the system, it minimizes microbial entry and reduces the risk of catheter-associated urinary tract infections (CAUTIs). Closed drainage bags are widely used in acute-care settings, long-term care, and home-based urological management for patients requiring continuous bladder drainage.
Closed-system bags typically consist of a flexible, medical-grade PVC or silicone reservoir, a non-reflux valve assembly, a sampling port, and a kink-resistant downstream tube. The catheter hub connects directly to the bag’s inlet port under aseptic conditions, ensuring that no external air or contaminants enter the system. Graduated volume markings on the bag's surface enable precise monitoring of urine output by nursing staff or caregivers, which is critical for fluid balance assessment and early detection of renal or cardiac dysfunction.
Key advantages of closed-system drainage bags include:
Infection Control: A sealed environment prevents introduction of pathogens during routine care or movement.
Accurate Monitoring: Clear, calibrated graduations allow for hourly or shift-based urine output measurements.
Convenience & Safety: Integrated sampling ports eliminate the need to open the system for specimen collection.
Patient Comfort: Lightweight, ergonomically shaped bags reduce tugging on the catheter and can be discreetly secured to the bed or wheelchair.
Proper maintenance protocols are essential to preserve system integrity and patient safety. Bags should remain below bladder level at all times to promote drainage by gravity and avoid backflow. Routine care involves emptying when the bag is two-thirds full, disinfecting the drainage spigot before and after use, and inspecting all connections for leaks or kinks every shift. Manufacturer guidelines usually recommend replacing the entire closed-system bag every 5–7 days or sooner if the bag becomes compromised.
| Component | Description & Care |
|---|---|
| Reservoir Material | PVC or silicone; inspect daily for discoloration or damage; replace per protocol (5–7 days). |
| Anti-Reflux Valve | Prevents urine backflow; test functionality during routine checks. |
| Sampling Port | Luer-lock port for sterile specimen collection; disinfect cap with alcohol swab before use. |
| Tubing & Connectors | Kink-resistant tubing; secure to leg or bed frame with straps; ensure no tension on catheter. |
| Graduated Markings | 100 mL increments up to 2 L; verify accuracy against nursing documentation every shift. |
| Drainage Spigot | Flip-seal or twist-seal design; disinfect before and after emptying; allow drip-free closure. |
By integrating closed-system urine drainage bags into standard clinical protocols—and reinforcing staff training on aseptic handling, bag placement, and timely replacement—healthcare teams can significantly lower infection rates while ensuring reliable fluid management and patient comfort.
| Learn more about urine drainage bags > |


 Français
Français Español
Español Products
Products

 About Us
About Us