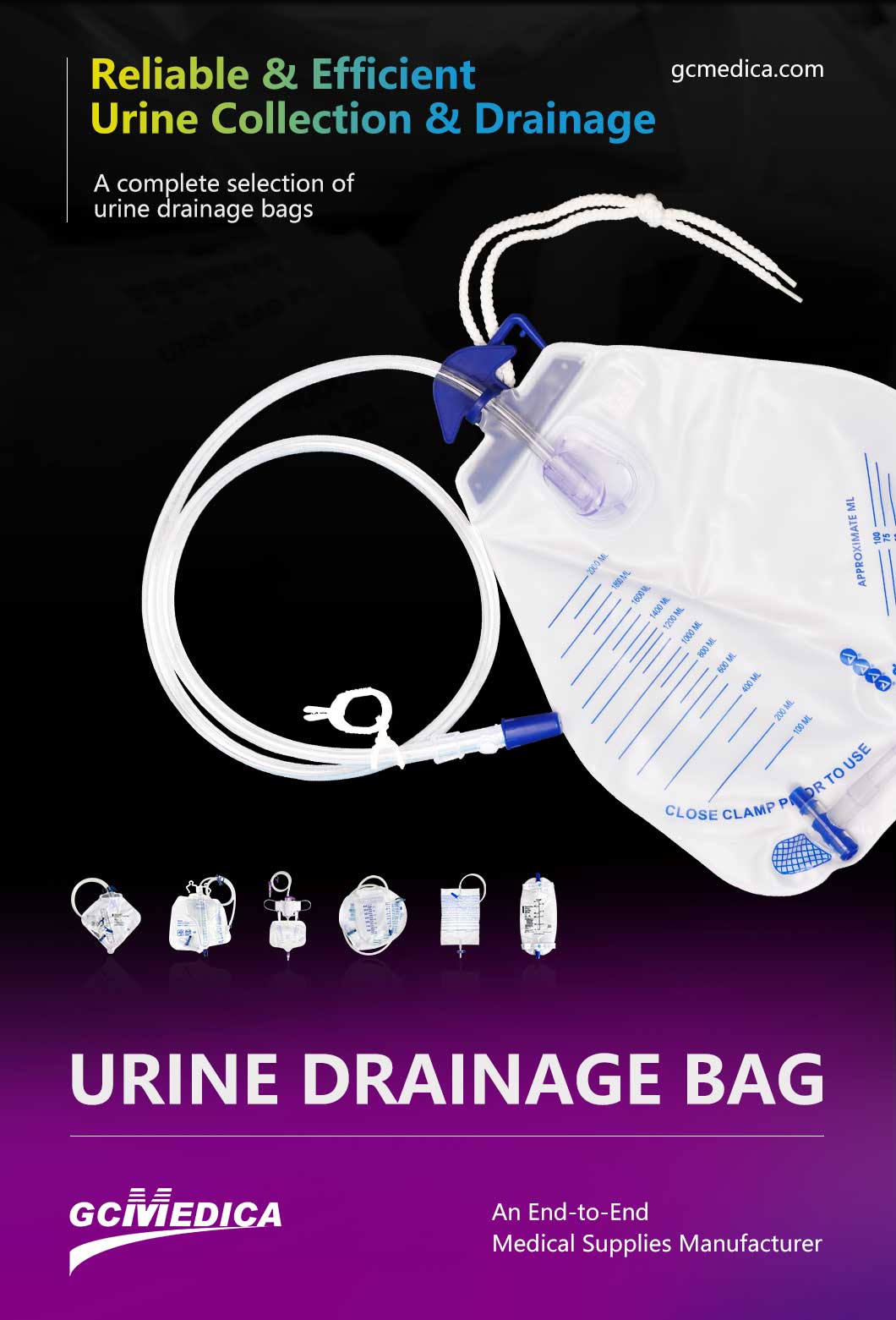
Urine meter drainage bags are indispensable in clinical settings, particularly in critical‐care units, long‐term care wards, and post‐operative recovery areas. They allow precise measurement of urinary output, a vital sign that reflects kidney function, fluid balance, and overall patient status. Most bags are made of medical‐grade PVC or TPU, offering flexibility, transparency for visual inspection, and compatibility with standard catheter connectors. Graduated markings (in milliliters) are printed or embossed to ensure accurate recording without disturbing the system integrity. A built‐in anti‐reflux valve prevents backflow, reducing the risk of infection and maintaining unidirectional drainage. Reinforced hanger hooks or belts permit secure attachment to bed rails or IV poles.
When choosing a drainage bag, factors to weigh include volume capacity, overall dimensions (to fit under‐bed or bedside use), tubing length (to accommodate different patient positions), material thickness (for durability), and additional features such as anti‐kink tubing, sampling ports, or odor‐control filters. Smaller‐capacity bags (500–1,000 mL) are suitable for ambulatory or pediatric patients, while higher‐capacity bags (2,000 mL and above) minimize bag changes for immobile or high‐output patients. Transparent windows and large‐print scales increase safety by reducing transcription errors. Lightweight construction and flat‐fold designs improve storage and transport convenience.
Below is a comparative size chart for four common urine‐meter drainage‐bag models. Dimensions are approximate and may vary slightly by manufacturer. Always verify compatibility with existing catheter systems and confirm regulatory approvals (e.g., FDA, CE) for your facility.
| Size Code | Capacity (mL) | Bag Dimensions (L × W) cm | Tubing Length cm | Material Thickness (mm) | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UMD-500 | 500 | 25 × 15 | 90 | 0.25 | Lightweight; pediatric scale; anti-kink tubing |
| UMD-1000 | 1000 | 35 × 18 | 100 | 0.30 | Standard adult use; reinforced hanger; sampling port |
| UMD-2000 | 2000 | 45 × 20 | 120 | 0.35 | Extended capacity; flat fold; odor filter |
| UMD-3000 | 3000 | 55 × 22 | 120 | 0.40 | High‐output patients; large graduation; anti‐reflux valve |
Chart Legend and Usage Notes:
Capacity (mL): Maximum fill volume; do not exceed 80% fill to allow for foam and movement.
Bag Dimensions: Length × width when laid flat; ensure adequate under‐bed clearance or wall‐mount space.
Tubing Length: From catheter connector to bag inlet; longer tubing increases risk of kinking—select the shortest practical length.
Material Thickness: Higher thickness enhances tear resistance but may slightly reduce bag flexibility.
Key Features: Highlights accessory elements such as sampling ports (for sterile specimen collection), anti‐kink springs, odor filters, and reinforced hangers.
Clinical Tips:
Always hang the bag below the level of the bladder to maintain gravity drainage.
Empty the bag before it reaches 75–80 % capacity to minimize tension on the tubing and reduce reflux risk.
Use sterile gloves when disconnecting sampling ports.
Inspect scales for legibility before use; replace bags that have faded graduations.
For mobile patients, consider compact or belt‐clip models to enhance comfort and mobility.
By understanding the specification differences—capacity, dimensions, tubing, material, and extra features—clinicians can optimize urine output monitoring, enhance patient comfort, and reduce the likelihood of catheter‐associated complications.
| Learn more about urine drainage bags > |


 Français
Français Español
Español Products
Products

 About Us
About Us