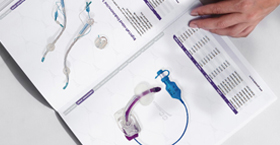
A Yankauer flange tip and an open suction tip are two of the most commonly used devices for airway and oral suctioning in clinical settings. Although both are designed to clear secretions and maintain airway patency, they differ in shape, suction efficiency, safety profile, and ideal applications.
A Yankauer tip features a rigid, curved metal or plastic shaft with a bulbous flange at the distal end. The flange has multiple small side holes around its circumference and one larger opening at the end. This design allows vigorous suctioning of thick secretions—such as saliva, blood, or mucus—without causing mucosal injury. The curved shape and firm flange also help dislodge adherent material from the oral cavity, surgical site, or tracheostomy stoma. Yankauer tips are typically used in operating rooms, emergency departments, and bedside for routine oral suctioning or coarse airway clearance. Because of the protected side‑hole design, there is less risk of the tip suctioning directly against tissue, which reduces trauma.
By contrast, an open suction tip (sometimes called a “straight tip”) is a simple, straight catheter or rigid tube with a single large opening at the distal end and no side ports. This open‑ended design maximizes flow rate and provides powerful suction, which can be advantageous for rapid removal of copious liquid or semi‑liquid secretions. However, the lack of protective side holes means the tip can more easily adhere to mucosa or laryngeal structures, potentially causing tissue injury or bleeding if advanced too far. Open tips are often preferred when fast evacuation of large-volume fluid (e.g., gastric contents, oral bleeding) is needed, but they require careful technique to avoid mucosal trauma.
Key factors influencing tip selection include the viscosity and volume of secretions, patient tolerance, and anatomical site:
Viscous secretions (thick sputum, blood clots): Yankauer flange tip
High‑volume liquid (gastric aspirate, fresh blood): Open tip
Oral cavity and surgical fields: Yankauer for safety and control
Rapid decompression (e.g., oral bleeding): Open tip for maximum flow
Below is a comparative summary:
| Feature | Yankauer Flange Tip | Open Suction Tip |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Curved shaft with bulbous flange and multiple side ports | Straight tube with single large distal opening |
| Suction Efficiency | Moderate flow, optimized for viscous secretions | High flow, optimized for large-volume liquids |
| Safety Profile | Lower risk of mucosal adherence or tissue injury | Higher risk of tissue suction if improperly used |
| Typical Uses | Oral suctioning, tracheostomy stoma, surgical field cleanup | Rapid removal of gastric contents, hemorrhage |
| Patient Comfort | Generally more comfortable and controlled | Can be more uncomfortable if tip contacts mucosa |
| Maneuverability | Curved shape facilitates access to oral/nasal cavities | Straight design may be easier in open cavities |
In practice, many clinicians carry both types and choose based on the immediate clinical context. A Yankauer tip often serves as the default for routine oral and airway suctioning because of its balance of efficacy and safety. When confronted with sudden, large‑volume fluid accumulation—such as in active bleeding or emesis—an open suction tip may be deployed to clear the airway rapidly. Proper training in suction technique and attention to catheter depth are essential to minimize complications such as hypoxia, mucosal trauma, or infection. By understanding the distinct characteristics and ideal indications for each tip, healthcare providers can optimize airway management and patient comfort.
| Yankauer Suction Tips> |


 Français
Français Español
Español Products
Products

 About Us
About Us