Medical Feeding: Enteral Feeding Tube vs. Nasogastric Tube

Introduction to Medical Feeding Tubes
In the realm of medical care, feeding tubes play a pivotal role in ensuring patients receive the nutrition they need when they are unable to eat by mouth. This necessity arises from a variety of conditions, ranging from acute illnesses and surgical recovery to long-term health issues that impair the natural process of eating. Among the diverse types of feeding tubes, enteral feeding tubes and nasogastric tubes stand out as critical tools in the arsenal of nutritional support.
Enteral feeding tubes are designed to deliver nutrition directly to the stomach or small intestine, bypassing the oral route entirely. This method is often utilized for patients who have a functioning gastrointestinal (GI) tract but are unable to ingest food orally due to reasons such as neurological impairments, physical obstructions, or severe weakness. On the other hand, nasogastric tubes, which are inserted through the nose and extend to the stomach, offer a temporary solution for feeding. They are typically used in situations where short-term nutritional support is needed, and the GI tract is still operational.
The distinction between enteral feeding tubes and nasogastric tubes is not just about their physical placement but also involves considerations regarding their use, benefits, and potential complications. By understanding these differences, healthcare providers can make informed decisions that align with the patient's specific medical needs and overall care goals. This article aims to shed light on these two types of feeding tubes, comparing their applications, advantages, and limitations to guide both healthcare professionals and caregivers in making the best choice for their patients or loved ones.
As we delve into the details of enteral feeding tubes and nasogastric tubes, we'll explore the nuances that differentiate them, the scenarios in which each is most appropriately used, and the factors that influence the selection process. Through this comparison, our goal is to provide a comprehensive understanding of these medical feeding options, empowering those involved in patient care to optimize nutritional support and, ultimately, patient outcomes.
What is an Enteral Feeding Tube?
Enteral feeding tubes are a lifeline for patients who require nutritional support but are unable to consume food orally. These tubes provide a direct method to deliver nutrition, fluids, and medications to the stomach or small intestine. Their design caters to long-term use, offering a safer and more comfortable alternative for patients needing sustained nutritional assistance.
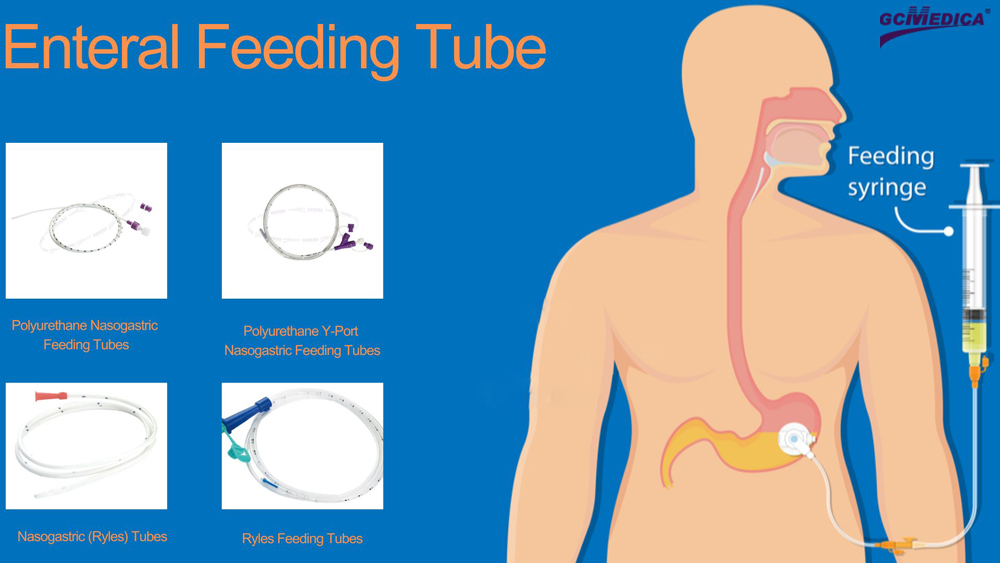
Types of Enteral Feeding Tubes:
PEG (Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy) Tubes: Inserted through the abdominal wall into the stomach, PEG tubes are often used for long-term feeding. They are ideal for patients with chronic conditions affecting their ability to eat, such as neurological disorders or head and neck cancers.
Jejunostomy Tubes: These tubes are inserted, typically surgically, directly into the small intestine. They're chosen for patients who cannot tolerate stomach feeding due to issues like severe reflux or gastric motility disorders.
Purpose and Benefits:Enteral feeding tubes are essential for patients who have a functioning GI tract but face challenges with oral intake. They help maintain nutritional status, improve medication administration, and enhance overall patient well-being. The direct delivery of nutrients to the GI tract also supports the preservation of gut integrity and promotes better absorption.
Considerations for Use:Choosing the right type of enteral feeding tube involves assessing the patient's overall health, nutritional needs, and the expected duration of tube feeding. It's crucial to consider the patient's lifestyle, care environment, and the potential for recovery or improvement in oral intake capability. Regular monitoring and care of the tube site are paramount to prevent infections and ensure the tube's functionality.
Enteral feeding tubes signify a profound step towards personalized patient care, enabling individuals to receive the nutrition they need despite medical challenges. By understanding the types and purposes of these tubes, healthcare providers can tailor nutritional support strategies that align with each patient's unique needs, ensuring they receive the best possible care.
What is a Nasogastric Tube?
Nasogastric tubes are a type of medical device used to deliver nutrition, fluids, and medications directly to the stomach through the nose. This method is typically employed for short-term feeding in patients who have a temporarily impaired ability to eat by mouth but possess a functioning gastrointestinal tract. The versatility and non-surgical placement of nasogastric tubes make them a vital tool in acute care settings, offering a quick and effective way to support patients' nutritional needs.
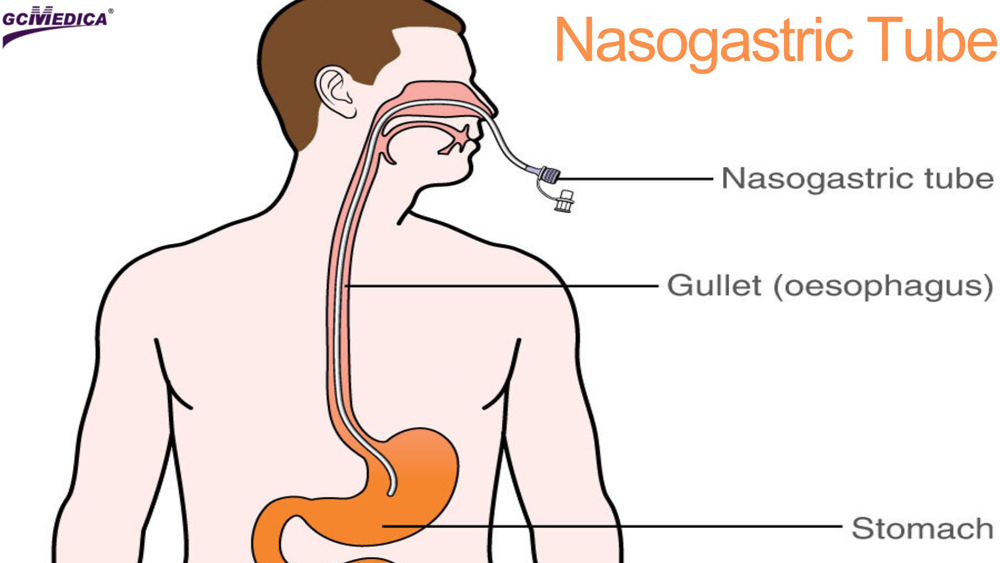
How Nasogastric Tubes Are Used:
Nutritional Support: For patients who cannot consume adequate nutrition orally due to illness, surgery, or other medical conditions.
Medication Administration: Allowing for the direct delivery of medications to patients unable to take them orally.
Gastric Decompression: Removing substances from the stomach in cases of bowel obstruction, poisoning, or preoperative preparation.
Advantages and Considerations:The primary advantage of nasogastric tubes is their ease of insertion and removal, which can be performed without the need for an operating room. This makes them an ideal choice for short-term use, typically ranging from a few days to several weeks. However, care must be taken to monitor for potential complications such as nasal discomfort, throat irritation, or the risk of aspiration pneumonia. Proper placement checks and regular monitoring are essential to ensure the tube remains correctly positioned and functional.
Situations Preferring Nasogastric Tubes:Nasogastric tubes are often the preferred choice in situations requiring temporary nutritional support or when the patient is expected to resume oral intake shortly. They are also selected for their utility in gastric decompression and emergency medication administration, highlighting their critical role in a broad range of medical scenarios.
Nasogastric tubes exemplify the adaptability of medical devices to meet diverse patient needs, offering a blend of convenience, efficacy, and safety. Understanding their use, benefits, and limitations is crucial for healthcare providers to optimize patient care and nutritional support strategies.
Comparing Enteral Feeding Tubes and Nasogastric Tubes
When it comes to providing nutritional support to patients unable to consume food orally, the choice between enteral feeding tubes and nasogastric tubes is crucial. Each type of tube offers distinct advantages and considerations, making it essential to understand their differences to select the most appropriate option for patient care.
Placement and Duration of Use:
Enteral Feeding Tubes are placed directly into the stomach or intestine through the abdominal wall. They are designed for long-term use, ranging from several months to years, and are suitable for patients requiring sustained nutritional support.
Nasogastric Tubes are inserted through the nose into the stomach and are intended for short-term use, typically a few days to several weeks. They are chosen for temporary nutritional support until the patient can resume oral intake or until a more permanent solution, like an enteral feeding tube, is deemed necessary.
Patient Comfort and Risk Considerations:
Enteral feeding tubes generally offer better patient comfort for long-term use, as they do not irritate the nasal passages or throat. However, their placement requires a surgical procedure, which carries its own risks and recovery time.
Nasogastric tubes can cause discomfort in the nose and throat and carry a higher risk of aspiration, especially in patients with compromised consciousness or gag reflex. Yet, their non-surgical placement makes them a quick and less invasive option for immediate nutritional support.
Pros and Cons Based on Clinical Needs:
Enteral Feeding Tubes:
Pros: More comfortable for long-term use, lower risk of aspiration, stable placement.
Cons: Requires surgery for placement, potential for complications at the insertion site.
Nasogastric Tubes:
Pros: Quick and easy to insert, adjustable, and removable without surgery.
Cons: Less comfortable for the patient, higher risk of nasal and throat irritation, increased risk of aspiration.
Selecting the right feeding tube involves a comprehensive evaluation of the patient's medical condition, the expected duration of feeding, and the goals of nutritional therapy. Collaboration among healthcare professionals, including doctors, nurses, and nutritionists, is vital to ensure that the chosen method of feeding adequately supports the patient's recovery and long-term health.
Choosing the Right Tube for Patient Care
Selecting the appropriate feeding tube for patient care is a critical decision that involves multiple factors. This choice significantly impacts the patient's recovery, comfort, and overall well-being. Here are key considerations to guide healthcare professionals in this decision-making process:
Factors to Consider:
Patient's Medical Condition: The underlying health issues and the reason for nutritional support need assessment. Conditions affecting the gastrointestinal tract, risk of aspiration, and the presence of reflux are crucial considerations.
Long-term vs. Short-term Use: Determine the expected duration of tube feeding. Nasogastric tubes are suitable for short-term, while enteral feeding tubes are designed for long-term nutritional support.
Patient's Lifestyle and Comfort: Consider the impact of the feeding tube on the patient's quality of life, including comfort, ease of care, and the ability to move and perform daily activities.
Role of Healthcare Professionals:Healthcare professionals play a vital role in selecting the most appropriate feeding method. This decision is a collaborative effort involving:
Nutritionists: to assess nutritional needs.
Physicians and Surgeons: to evaluate medical conditions and the feasibility of tube placement.
Nursing Staff: to provide insights on daily care and patient comfort.
The Patient and Family: When possible, involving the patient and their family in the decision-making process is vital for ensuring that the chosen method aligns with the patient's preferences and care goals.
Conclusion
The choice between an enteral feeding tube and a nasogastric tube is a significant one, with implications for the patient's nutritional support, recovery, and quality of life. This article has explored the critical differences between these two types of tubes, including their placement, duration of use, and suitability for various patient conditions.
In summary, enteral feeding tubes are typically used for long-term nutritional support and offer stability and reduced risk of aspiration. In contrast, nasogastric tubes are ideal for short-term use, providing a non-surgical option for immediate nutritional, fluid, and medication delivery. The selection process must consider the patient's medical condition, the anticipated duration of feeding, and the impact on the patient's comfort and lifestyle.
Ultimately, the decision on which feeding tube to use should be made with a comprehensive understanding of the patient’s specific needs and in close collaboration among healthcare professionals, the patient, and their family. Choosing the right feeding tube is a crucial step towards ensuring optimal patient care and facilitating recovery, underscoring the importance of informed, patient-centered medical decisions.
Related News

